To the laboratory website
Outline
We conduct research and education on humans from a holistic life view by applying information science and engineering technology. Our aim is to directly contribute to the progress of medical diagnostic and therapy, and to the promotion of the people’s QOL (quality of life). To realize this aim, we develop and upgrade diagnostic/treatment technologies, and train professionals who can support such development.
The Photonics group is developing diagnostic technology using light such as nonlinear Raman imaging, transillumination imaging, optical tomography, and fluorescence imaging.
The Ultrasound group is developing diagnostic techniques using ultrasound and cell-level treatment techniques using microbubbles.
Staff with the backgrounds of biomedical engineering, photonics, and electronic/information/communication engineering work together to promote interdisciplinary research and education.

Research
Photonics Group
Visualization of tissues / lesions by molecular vibrations
In pathological diagnosis, diagnosis is made by specimens from tissue and cells of lesions collected from the patient’s body. However, since tissues and cells are almost colorless, they must be stained. Staining affects living cells and is hard to apply to humans. Also, the staing procedure often requires long time. Therefore, if tissues and lesions can be identified without staining, diagnosis and treatment can be performed more safely and quickly.
A molecule vibrates because its atoms (mass points) are connected by chemical bonds (springs), and the vibrational frequencies of a molecule is sensitive to the spcices and structure. Using the molecular vibrations, we are developing imaging systems that distinguishes and visualizes cells and tissues and applies it to diagnosis.
Generally used spontaneous Raman scattering is extremely weak, so it takes a long time to measure. By using nonlinear Raman scattering, we are developing high-speed imaging systems that distinguishes tissues and lesions without staining.
Development of synchronous ultrashort pulse lasers
Nonlinear Raman scattering imaging requires special light sources. It is necessary to irradiate the sample with two laser pulses that have a narrow spectral band and short pulse duration (picoseconds) with different wavelengths. It is also necessary to scan the wavelength of one laser source at high speed. By developing such laser light sources, we are trying to achieve unstained imaging that can be used in the medical field.
Optical transillumination imaging
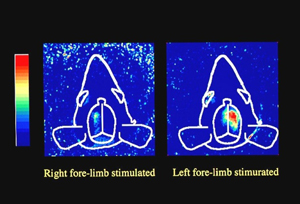
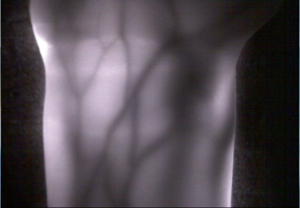
Optics-based biomedical measurement is highly valued as new diagnostic technology because it not only enables measurement of the structure of internal organs, but also of vital function. Transillumination imaging in particular is feasible with very simple and safe equipment. Research is underway to use this technology for functional imaging of the brain and internal organs of lab animals, to support the treatment of people whose blood vessels are hard to see, and to authenticate veins that enhance information security in the future.
Optical tomography
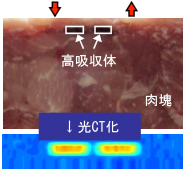
X-ray CT and other tomography technologies are now widely used, but there are problems in terms of radiation exposure and device scale. The development of optical tomography, which is safe for patients and requires only compact equipment, is underway.
Fluorescence imaging
Fluorescent materials that selectively accumulate in cancer cells as well as fluorescent materials for angiography have been developed. We are developing techniques for transcutaneous fluorescent imaging of in vivo functions. Blurring of the transcutaneous fluorescent image of deep structure can be greatly improved using the point spread function derived in our research.
Diagnosis and treatment using microbubbles
Nano-size microbubbles (1/10,000 mm) and micron-size microbubbles (1/1,000 mm) are now widely used as ultrasound contrast agents. The agent injected inside a vessel enables sensitive detection of small lesions. Microbubbles are also used as a carrier of drug delivery or gene transduction, and make it possible to treat lesions in the depth of the body. This technique is attracting attention as a method to provide a safe local treatment. We are conducting research in diverse ways to put this technology to practical use.
Ultra high-speed observation of microbubble behavior
Bubbles show repetitive expansion and contraction under ultrasound exposure and then concentrate energy that they received from the ultrasound. We observe bubble oscillation at a maximum framing rate of 20 million fps to examine the mechanism.
Behavior of microbubbles of two microns in diameter that have been captured by framing rate of 16 million fps. The behavior of microbubbles under ultrasound exposure was elucidated by stretching the observation time 2 million times.
Clarification of the effects of microbubble behavior on cells
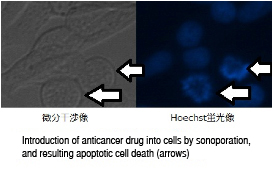
If a cell with adjacent microbubbles is exposed to ultrasound, the cell membrane permeability is temporally increased, and the drug and genes that are not usually taken up can be introduced into the cell. This phenomenon is called sonoporation and is expected to be applied to the drug delivery system (technology that causes a drug to only act on the cells that need the drug) for anticancer drugs and gene transduction to cells.
The images show that sonoporation allows the uptake of an anticancer drug into cancer cells, which then leads the cells to apoptosis (cell suicide).
Positional control of microbubble by optical tweezers
In the basic research on cell treatment using microbubbles, it is convenient if the position of the microbubbles can be controlled freely. However, it is difficult to move bubbles smaller than blood cells. Optical tweezers system was developed that can make tweezers beams with various shapes using holograms, thereby enabling the bubble trapping.
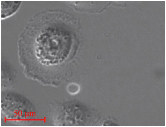
A doughnut-shaped optical beam made by holography can be observed under a cell. A microbubble is trapped inside the doughnut beam. Cell treatment can be achieved by moving the microbubble to the vicinity of a cell that needs treatment and exposing it to ultrasound.
Development of microbubbles
Transduction of drugs and genes into cells can be realized efficiently by loading them to microbubbles. Since current anticancer drugs cause cell death both in cancerous and normal tissues, chemotherapy causes serious damage on the patient. If microbubbles loaded with anticancer drug accumulate only in cancerous tissues, tissue selective chemotherapy can be realized.
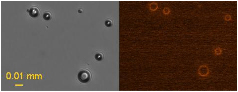
Micrographs of bubbles. Both are images of the same bubbles. In the left micrograph, bubbles are visualized as black sphere with bright spot at the center. The right micrograph shows the bubbles with red fluorescence around them, indicating the anticancer drug is loaded with their shell.
Study on sonoporation phenomenon in in vivo condition
We have been studying the sonoporation phenomenon using cultured cells. However, our goal is to realize efficient sonoporation inside the living body. To this end, it is necessary to investigate the differences in the sonoporation effects between cells in petri dishes and cells in in vivo condition. We therefore established a technique to culture cells on a soft gel scaffold that simulates living tissues, and difference in sonoporation effects is investigated.
Study on the mechanisms to produce premature ventricular contraction (PVC)

A suspension of microbubble is a very safe contrast agent, but several studies have reported that exposure of diagnostic ultrasound increases probability to generate PVCs. To improve safety of ultrasound contrast agents, we are now studying the mechanisms of PVC generation using cultured cardiac myocytes isolated from neonatal rats.
Cultured cardiac myocyte samples with autonomous pulsation can be created using myocytes isolated from neonatal rats. This is the important experimental technique that realizes direct observation of PVC generation induced by ultrasound exposure in the presence of microbubbles adjacent cardiac myocytes.
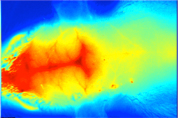
Visualization of invisible ultrasound
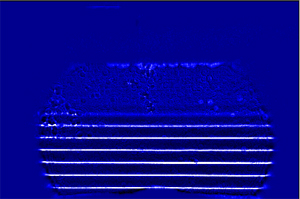
Ultrasound is widely used both in fields of medical diagnosis and therapy. During the development of diagnostic and therapeutic ultrasound devices, accurate evaluation of their ultrasound fields is essential. We have been studying a new optical method for visualizing the ultrasound fields (sound pressure distribution), and its usefulness is confirmed.
Ultrasound field propagating in water. The areas with high sound pressure are shown in white and the areas with negative pressure are shown in black. The ultrasound field, which is invisible to the naked eye, is propagating from the bottom to top.
Examples of research equipment
Optical experimental system

Femtosecond laser
Tunable laser
Picosecond streak camera
Cooled CCD camera
Time-lapse light microscope
P1 level laboratory
Clean bench
Cell culture equipment
Inverted light microscope
Full automatic microscope
Sonoporation experiment system
Optical tweezers equipment
Diagnostic ultrasound equipment
Therapeutic ultrasound equipment
Ultra high-speed imaging system
Image subtraction Schlieren system
Knowledge and technologies
Medical optics technologies
- Basic optical measurement technology
- Picosecond time-resolved measurement technology
- Optical simulation technology
- Optical tweezers technology
- Image subtraction Schlieren observation
Bio-related technologies
- General cell culture technology
- Isolation/culture technologies for cardiomyocytes
- Gene amplification/transduction technologies
Observation technologies
- Optical microscope technology
- Fluorescent observations technology
- Time-lapse observation technology
- Scanning electron microscope technology
- Ultra high-speed imaging technique
Medical ultrasound technology
- Basics and applications of ultrasound measurement
- Acoustic field measurement technology
- Basics and applications of ultrasound diagnostic equipment
- Basics and applications of ultrasound therapeutic equipment
- Ultrasound-based drug/gene transduction technology
Data analysis/device control technologies
- Technology to control measurement devices using LabVIEW and MATLAB, data analysis technology for experimental data
Keywords
Biomedical engineering, diagnostic/therapeutic technology development, human information, medical optics, medical ultrasound
Members
- Professor: Mamoru Hashimoto
- Associate Professor: Nobuki Kudo
- Assistant Professor: Yuji Kato
- Postdoctoral Fellow: 1
- Doctoral students: 3; master’s students: 8; undergraduates: 5
Contact
Address: M Bldg. 3F, Graduate School of Information Science and Technology, Hokkaido University
Kita 14-jo, Nishi 9-chome, Kita-ku, Sapporo, 060-0814
Prof. Hashimoto: Ext. 6857, E-mail:hashimoto@ist.hokudai.ac.jp
Associate Prof. Kudo: Ext. 6157, E-mail:kudo@ist.hokudai.ac.jp
Assistant Prof. Kato: Ext. 7229, E-mail:kato@ist.hokudai.ac.jp